Understanding Wire Galvanization An Essential Process for Durability and Protection
Wire galvanization is a process that involves coating steel wire with zinc to protect it from corrosion. This technique is vital in various industries, as it significantly enhances the lifespan and durability of wire products. In this article, we delve into the principles of wire galvanization, its processes, applications, and benefits.
What is Galvanization?
Galvanization is the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron to prevent rusting. The name originates from the Italian scientist Luigi Galvani. There are several methods for galvanizing wire, including hot-dip galvanization, electro-galvanization, and used to be referred as the most common galvanizing processes.
1. Hot-Dip Galvanization In this method, the wire is submerged in a molten zinc bath. The heat from the molten zinc causes a metallurgical reaction that creates a protective layer around the wire. This method is favored for its robust coating, which adheres strongly to the wire surface and provides long-term protection against corrosive environments.
2. Electro-Galvanization Unlike hot-dip galvanization, electro-galvanization involves electrolytic deposition of zinc onto the wire. The wire is placed in an electrolyte solution, and an electric current drives zinc onto the wire’s surface. Although this method results in a thinner coating compared to hot-dip galvanization, it provides a smooth finish that is often preferred for aesthetic applications.
Applications of Galvanized Wire
Galvanized wire has a wide array of applications across multiple sectors, including construction, agriculture, manufacturing, and telecommunications. Some of the key applications are
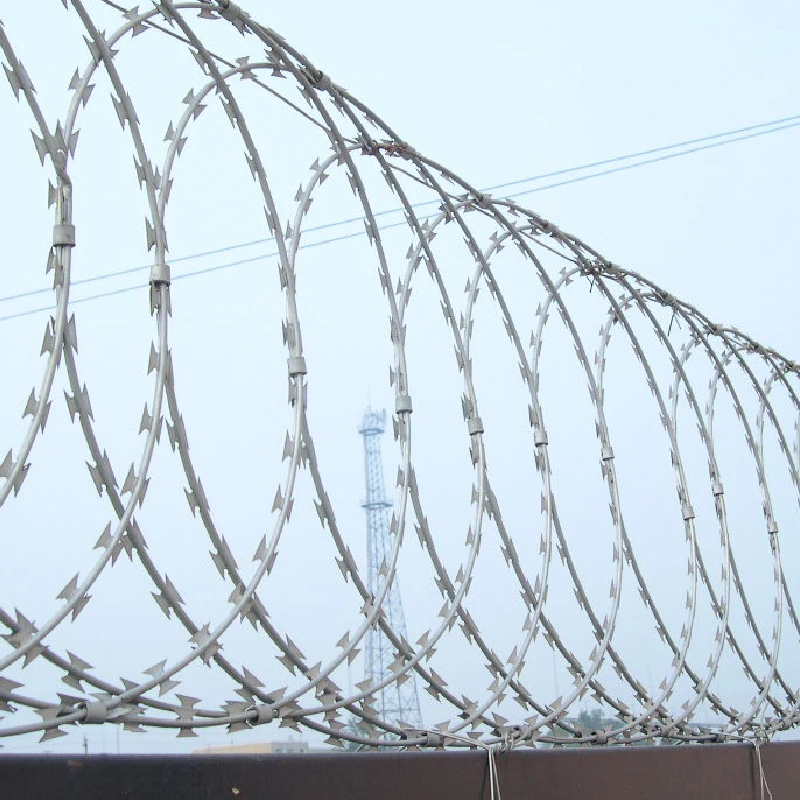
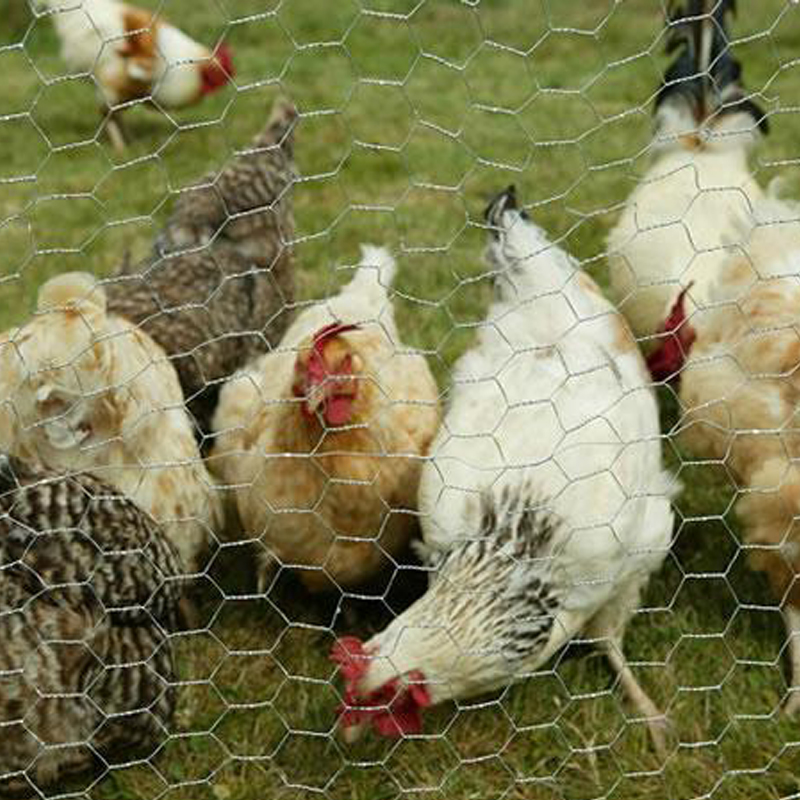
- Fencing Galvanized wire is commonly used in fencing due to its excellent resistance to rust. Chain-link fences, barbed wire, and agricultural fencing often utilize galvanized wire to ensure durability against weathering.
- Construction In the construction industry, galvanized wire is essential for reinforcing concrete and masonry work. It is widely used in wire mesh and rebar applications to enhance structural integrity.
wire galvanised

- Electrical Wiring Galvanized wire is also employed in electrical wiring, particularly for overhead power lines. The zinc coating prevents corrosion, ensuring a reliable and long-lasting connection in various weather conditions.
- Craftsmanship Artists and craftsmen often use galvanized wire for various projects. Its malleability and resistance to rust make it ideal for sculptures, jewelry, and other artistic creations.
Benefits of Using Galvanized Wire
The benefits of using galvanized wire are numerous. Here are some significant advantages
1. Corrosion Resistance The primary purpose of galvanization is to provide protection against rust and corrosion. This is particularly important in environments that are exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme weather conditions.
2. Longevity Galvanized wire has a significantly longer lifespan compared to non-galvanized wire. This durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, thus lowering overall costs for consumers and industries.
3. Maintenance-Free Once galvanized, the wire requires minimal maintenance. This feature is especially appealing to applications where regular upkeep is challenging or impractical.
4. Cost-Effective Although the initial cost of galvanized wire may be higher than non-galvanized options, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacements often make it a more economical choice.
Conclusion
Wire galvanization is a crucial process that enhances the longevity and durability of steel wire. With various methods like hot-dip and electro-galvanization, it provides effective corrosion resistance, making it an ideal solution for a broad spectrum of applications—from construction to crafting. As industries continue to seek durable materials suited to various environmental conditions, galvanized wire remains a reliable choice that combines performance with cost-effectiveness. Whether it’s securing a fence, reinforcing a structure, or creating artistic pieces, galvanized wire is a testament to the importance of protection and longevity in material science.